Deep Web Links and Tor are a Human Right in the Fight Against Censorship
In a digital world where digital censorship is on the rise, accessing information openly becomes an important part of preserving individual freedom and human rights. Deep web links and Tor, the anonymous network, have turned out as powerful tools in the fight against censorship. Their existence empowers individuals to exercise their right to access, share, and spread information without fear of surveillance or counterattack.
| Key Takeaways Accessing deep web links and Tor is a human right in the fight against censorship. Tor is an anonymous network that allows users to browse the internet without revealing their real identities. Always use a VPN with Tor to enhance your anonymity further. Journalists, activists, or whistleblowers usually use Tor to keep their identities anonymous and share vulnerable information about wrongdoing. Use Snowflake pluggable transports to access the Tor network if authorities block direct access to Tor in your country. |
Understanding the Importance of Privacy and Freedom of Information
In every democratic society, privacy and freedom of knowledge are the fundamental rights of every individual. In an era where surveillance and monitoring are usual, the need for secure and private communication channels has never been more essential. Deep web links and Tor provide people with the means to bypass suppressing and access information that is usually hidden from the public eye.
The deep web is different from the surface web we commonly use and is not indexed by search engines. It consists of websites and content that are not easily accessible via ordinary browsers. On the other hand, the Tor network is a decentralized network that allows users to browse the internet anonymously. With these unique tools, people can explore the deep web and access a wealth of knowledge that may be censored or restricted in their country.
How the Deep Web Links and Tor Work Together
The deep web, often referred to as the dark web, is a hidden world of the internet that cannot accessed via regular search engines. It is a wide network of websites and services that are not indexed by Google and other search engines, making it difficult to discover unless you know where to find them. Deep web links operate on encrypted networks and require a specific browser like Tor or configurations to access.
The full form of Tor is The Onion Router is an anonymous network that allows users to explore the internet without revealing their true identities. It operates by enciphering and routing internet traffic through a series of volunteer-operated servers known as nodes. Every node in the network only knows the IP address of the previous node and the next node. Making sure that no single entity can trace a user’s complete online browsing.
Steps to Access the Deep Web and Use Tor Safely and Securely
Deep web links and Tor provides a means to circumvent censorship and protect privacy. It is essential to use these tools securely and safely. Here are some steps to follow when accessing the darknet and using Tor.
- From the Tor official site, download and install the Tor browser.
- Ensure that the Tor browser is up to date to take advantage of the latest security features.
- Use a Virtual Private Network (VPN) to enhance your anonymity more.
- Avoid clicking or downloading files on suspicious links that could endanger your security.
- Be careful of the websites you visit, and take caution when sharing personal information.
- Regularly clear your browsing history and cookies to minimize the risk of being tracked.
- Regularly updated antivirus software to secure your digital presence in the deep web links and Tor.
Deep Web Links and Tor as Tools for Fighting Censorship
Deep web links and Tor have become precious tools for individuals living in countries with strict internet censorship. These tools give a lifeline to access information that others would block by oppressive regimes. By bypassing government controls, people can freely access news, social media, and other sources of information that are critical for staying informed and challenging the existing condition.
Moreover, deep web links and Tor have become necessary for activists, journalists, and human rights organizations. They provide secure communication, allowing activists to coordinate their efforts without fear of interception or surveillance. Whistleblowers can share sensitive information anonymously, exposing corruption and misconduct without threatening their safety. By offering a platform for dissent and uncensored knowledge sharing, deep web links and Tor empower individuals to challenge systemic restriction and fight for greater transparency.
Government Surveillance and the Need for Secure Communication
In an era of extensive government surveillance, the need for secure communication has never before been greater. Deep web links and Toe provides a way to communicate safely without the fear of seizure or surveillance. By encrypting internet traffic and routing it via a series of nodes, Tor ensures that the user’s online activities remain private and protected from prying eyes.
Government surveillance poses a serious threat to individual freedoms and the right to privacy. By using deep web links and Tor, citizens can protect themselves from unjustified observation and maintain control over their data. These tools allow individuals to take their right to communicate freely and securely, ensuring that their thoughts, ideas, and opinions remain their own.
When using Tor, it is advisable to use additional security measures such as a VPN virtual private network to enhance anonymity further and protect against potential threats. Users should also be careful of the information they share while using Tor, and anonymous networks can endanger even themselves if proper precautions are not exercised.
Case Studies of Individuals and Organizations Using the Deep Web and Tor for Activism
Numerous individuals and organizations have utilized the deep web and Tor to champion causes and challenge censorship around the world. One prominent instance is the case of Chelsea Manning, a former U.S. Army intelligence analyst who submits classified documents to WikiLeaks. Manning utilized Tor to secure her identity while leaking sensitive data to the public, exposing government misuse of power and sparking a global conversation on transparency.
Another prominent example is the Arab Spring, a series of protests and uprisings that swept across the Middle East and North Africa in 2010 and 2011. During this time, protestors used deep web links and Tor to organize and communicate, bypassing government monitoring and censorship.
Similarly, organizations like Reporters without Borders have set up mirror websites on the deep web to provide access to uncensored news in countries where traditional websites are blocked. By leveraging the anonymity and encryption offered by the deep web and Tor, these organizations can ensure that individuals living under oppressive regimes can access vital information without fear of reprisal.
Debunking Misconceptions about the Deep Web and Tor
The deep web and the Tor network are often considered illicit activities and criminal behavior platforms. At the same time, some illegal activities indeed take place on the dark net. It is essential to separate the technology from the actions of a few people. The deep and Tor are neutral platforms that can be used for either good or bad purposes. Like the internet itself can be utilized for illegal activities, it is also a platform for education, communication, and innovation.
It is important to debunk the misconception that the deep web and Tor are just for criminals. In reality, these platforms are used by people seeking privacy, security, and freedom of thought. Journalists, whistleblowers, activists, and normal citizens can all take advantage of the ability to access information without fear of retaliation. By understanding the true landscape of the darknet, we can better appreciate their importance in upholding our democratic values.
The Legal and Ethical Implications of Using Deep Web Links and Tor
The use of deep web links and Tor upholds significant legal and ethical questions. On one hand, these tools enable individuals to exercise their right to privacy and freedom of information. They allow for the sharing of information and the exposure of misuse of power. On the other hand, it is also used for illicit activities, such as drug trafficking or the spreading of child pornography.
Governments and law enforcement agencies face a difficult challenge in balancing the need to protect citizens while respecting their rights. Some countries have decided to ban or restrict the use of deep web links and Tor, citing concerns over national security or public safety. However, these measures often violate the rights of individuals and limit their ability to access information freely. Contrasting the correct balance between security and privacy is a complicated task that requires careful attention.
Protecting your Identity and Staying Anonymous on the Deep Web
When accessing the deep web, it is crucial to take measures to protect your identity and maintain anonymity. Here are some tips to help you stay safe:
- Use a false name or online alias instead of your real name.
- Avoid sharing personal information that can identify your identity.
- Encrypt your communications using tools like PGP (Pretty Good Privacy).
- Be mindful when interacting with others online, and avoid sharing too much about yourself.
- Regularly update your passwords and make a unique and strong one.
- Take additional security steps, like two-factor authentication.
The Future of the Deep Web and Tor in the Fight Against Censorship
With governments tightening their grip on the internet, individuals and organizations will rely on these tools to bypass censorship, share uncensored knowledge, and challenge oppressive regimes.
As the fight against censorship increases, the role of deep web links and Tor will continue to grow in importance. With governments tightening their grip on the internet, individuals and organizations will rely on these tools to bypass censorship, share uncensored knowledge, and challenge oppressive regimes.
The future of the deep web and Tor lies in continued innovation and development. Efforts to make these tools more user-friendly and accessible will be crucial in ensuring that they reach a wider audience. Additionally, ongoing research and advocacy will be necessary to address the legal and ethical concerns surrounding their use and to promote responsible and transparent practices.
How to Access Tor if Your Country’s Government Blocks Direct Access to the Tor Network
The onion router Tor network remains one of the most productive censorship avoidance technologies. Millions of individuals use the Tor browser regularly to access the internet without fear of monitoring and censorship.
Mostly, people get the Tor browser from their official site and start connecting to a relay. But most countries, such as Russia, Iran, Belarus, China, and Turkmenistan, block direct access to the Tor network. In those countries, people have to use Tor bridges to bypass national firewalls to access the Tor network. A large number of individuals use bridges daily to avoid censorship and regional restrictions.
Of course, securities, where Tor services are banned, are constantly trying to find the IP address of bridges and block them to far away individuals from accessing Tor. Bridge connections can also be fingerprinted or identified as connections to the Tor network by authorities using deep packet inspection. To cope with this, Tor has a quick-witted solution called pluggable transports. Pluggable transports conceal your Tor connection as typical traffic to a well-known web service like Google or Skype and smuggle your Tor connection inside of the apparently innocuous traffic.
In former times, running a pluggable transport was challenging to set up, requiring a server and a lot of time and technical knowledge. After the launch of a new pluggable transport named Snowflake, anyone can run a pluggable transport in their browser with just a few clicks and support people all over the globe access the unrestricted internet.
How Snowflake Works
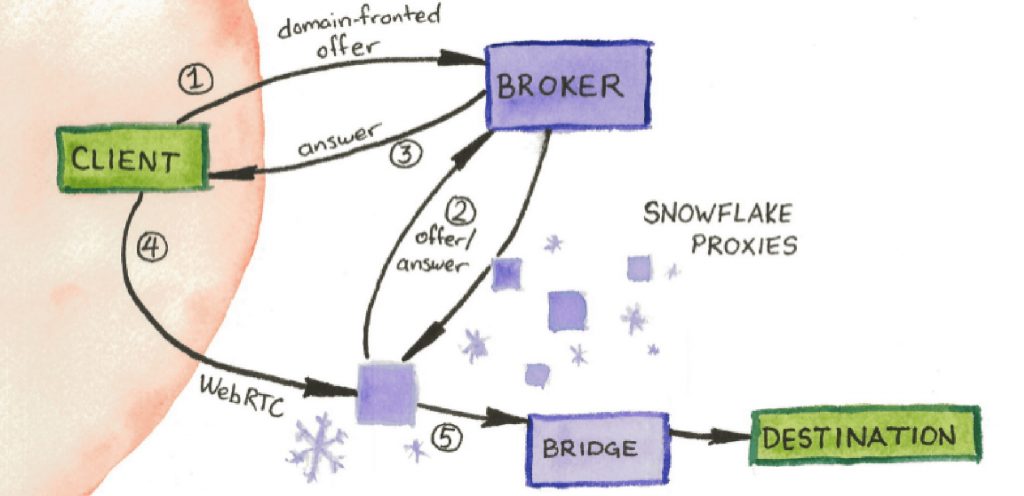
Snowflake is made up of three elements: volunteers managing Snowflake proxies, Tor clients who want to connect to the hidden internet, and a broker that sends its proxies to clients. Volunteers ready to help clients on censored networks can help by circulating short-lived proxies on their standard browsers.
When you start Snowflake, your browser will contact the broker and let it know that you are willing to accept P2P (peer-to-peer) connections from people searching to access Tor. Then, clients who are on a restricted network can communicate with the broker and ask for a proxy. The broker will shortly hand them your IP address, and then the user will make a direct connection to your computer using WebRTC. This technology is used by Zoom, Skype, and many other peer-to-peer web connections. Then, your computer will forward traffic from the client to the Tor network.
So Why Authorities can’t Block Domain Fronting
The noticeable weak point here is the broker server. Why couldn’t a territory block the broker IP since it is very popular? The answer is a technique known as domain fronting. The domain fronting lets the client request that like a normal web request for google.com, and because of HTTPS, the request is able to hide its host header, which is actually for a random web service hosted on Google’s cloud. That service is known as Snowflake Broker.
To shut down Snowflake, a region or country would have to terminate all of Google or every IP address outside of the network, basically a complete breakdown of the internet. Of course, territories have continuously shown their willingness to do exactly that, but it is a much higher price to pay than restricted Tor.
The security risks for the snowflake proxy operator are the least. The Snowflake client will not be able to reach out to your PC in any way or monitor your network traffic, and you will not be able to see their traffic. From the outlook of your ISP, it will look like you are connecting to a Tor bridge, which, if you are using a Snowflake proxy, should be legal and unrestricted in your region. No more concerns is using a Snowflake proxy than using a Tor browser.
Snowflake aims that everyone can exercise their freedom of expression anywhere in the world. However, it takes no technical knowledge to run, so if you are in a restricted region, you can install the Snowflake browser add-on, or if you run a server, you can use the standalone version in Go.
Conclusion: Empowering Individuals via the Deep Web and Tor
In a world frustrated by censorship and surveillance, deep web links and Tor provide individuals a lifeline to freedom of expression and access to valuable information. By grabbing these tools as a human right, people regain control over their online activities and protect their right to privacy.
Deep web links and Tor empower people to challenge censorship, promote transparency, and fight for a more open and democratic society. As we explore an increasingly interconnected world, preserving access to the deep web and Tor is essential for safeguarding individual liberties and ensuring the free flow of information.
In the digital age, the fight against censorship has become gradually significant. Governments and corporations alike attempt to control what information we can access, limiting our freedom of expression and blocking our ability to communicate. However, there is a digital underground that is challenging these limitations – the deep web links and the Tor network.
